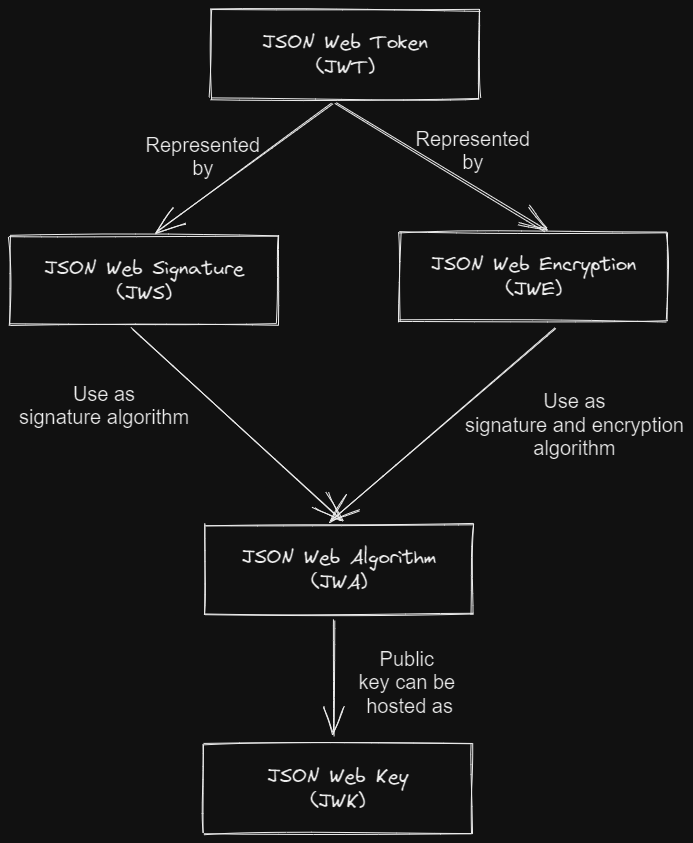
JSON Web Token 或 JWT 作为服务之间安全通信的一种方式而闻名。JWT 有两种形式,JWS 和 JWE。本文将探讨 Java Spring Boot 中 JWT 的实现。
JSON Web Token 或 JWT 作为服务之间安全通信的一种方式而闻名。JWT 有两种形式,JWS 和 JWE。它们之间的区别在于 JWS 的有效负载没有加密,而 JWE 是加密的。
本文将探讨 Java Spring Boot 中 JWT 的实现。如果您想了解更多关于 JWT 本身的信息,您可以在此处访问我的另一篇文章。本文中的代码托管在以下 GitHub 存储库中:
https ://github.com/brilianfird/jwt-demo 。
图书馆
对于本文,我们将使用该jose4j库。jose4j是 Java 中流行的 JWT 库之一,具有完整的功能。如果您想查看其他库(无论是否用于 Java),jwt.io已经编译了它们的列表。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bitbucket.b_c</groupId>
<artifactId>jose4j</artifactId>
<version>0.7.12</version>
</dependency>在 Java 中实现 JWS
JSON Web Signature (JWS) 由三部分组成:
- 何塞标题
- 有效载荷
- 签名
让我们看一个 JOSE 标头的示例:
{
alg:"HS264"
}
JOSE 标头存储有关如何处理 JWS 的元数据。alg存储有关 JWT 使用哪种签名算法的信息。
接下来,让我们检查有效载荷:
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "Brilian Firdaus",
"iat": 1651422365
}
JSON 有效负载存储我们要传输到客户端的数据。它还存储了一些 JWT 声明,以供我们验证。
在上面的示例中,我们将三个字段注册为 JWT 声明。
sub表示用户的唯一idname表示用户名iat表示我们在一个 epoch 中创建 JWT 的时间
最后一部分是签名,它是使 JWS 安全的部分。通常,JWS 的签名将采用字节的形式。让我们看一个 Base64 编码签名的示例:
qsg3HKPxM96PeeXl-sMrao00yOh1T0yQfZa-BsrtjHI
现在,如果我们看到上面的三个部分,您可能想知道如何将这三个部分无缝地传递给消费者。答案是紧凑的序列化。使用紧凑序列化,我们可以轻松地与消费者共享 JWS,因为 JWS 将成为一个长字符串。
Base64.encode(JOSE Header) + "." + Base64.encode(Payload) + "." + Base64.encode(signature)
结果将是:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjIwMjItMDUtMDEifQ.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkJyaWxpYW4gRmlyZGF1cyIsImlhdCI6MTY1MTQyMjM2NX0.qsg3HKPxM96PeeXl-sMrao00yOh1T0yQfZa-BsrtjHI
紧凑序列化部分在 JWT 规范中也是强制性的。所以为了让 JWS 被认为是 JWT,我们必须进行紧凑的序列化。
未受保护
我们将探讨的第一种 JWS 是不受保护的 JWS。人们很少使用他的 JWS 类型(基本上只是一个常规的 JSON),但让我们首先探索一下以了解实现的基础。
让我们从创建标题开始。与之前使用算法的示例不同HS256,现在我们将不使用算法。
生成不受保护的 JWS
@Test
public void JWS_noAlg() throws Exception {
JwtClaims jwtClaims = new JwtClaims();
jwtClaims.setSubject("7560755e-f45d-4ebb-a098-b8971c02ebef"); // set sub
jwtClaims.setIssuedAtToNow(); // set iat
jwtClaims.setExpirationTimeMinutesInTheFuture(10080); // set exp
jwtClaims.setIssuer("https://codecurated.com"); // set iss
jwtClaims.setStringClaim("name", "Brilian Firdaus"); // set name
jwtClaims.setStringClaim("email", "brilianfird@gmail.com");//set email
jwtClaims.setClaim("email_verified", true); //set email_verified
JsonWebSignature jws = new JsonWebSignature();
jws.setAlgorithmConstraints(AlgorithmConstraints.NO_CONSTRAINTS);
jws.setAlgorithmHeaderValue(AlgorithmIdentifiers.NONE);
jws.setPayload(jwtClaims.toJson());
String jwt = jws.getCompactSerialization(); //produce eyJ.. JWT
System.out.println("JWT: " + jwt);
}
让我们看看我们在代码中做了什么。
- 我们设置了一堆声明(
sub,iat,exp,iss,name,email,email_verified) - 我们将签名算法设置为
NONE,算法约束设置为,NO_CONSTRAINT因为jose4j会抛出异常,因为算法缺乏安全性 - 我们将 JWS 打包在紧凑序列化中,它将生成一个包含 JWS 的字符串。结果是一个 JWT 编译的字符串。
让我们看看我们通过调用得到什么输出jws.getCompactSerialization():
eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJzdWIiOiI3NTYwNzU1ZS1mNDVkLTRlYmItYTA5OC1iODk3MWMwMmViZWYiLCJpYXQiOjE2NTI1NTYyNjYsImV4cCI6MTY1MzE2MTA2NiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9jb2RlY3VyYXRlZC5jb20iLCJuYW1lIjoiQnJpbGlhbiBGaXJkYXVzIiwiZW1haWwiOiJicmlsaWFuZmlyZEBnbWFpbC5jb20iLCJlbWFpbF92ZXJpZmllZCI6dHJ1ZX0.
如果我们尝试对其进行解码,我们将获得带有我们之前设置的字段的 JWS:
{
"header": {
"alg": "none"
},
"payload": {
"sub": "7560755e-f45d-4ebb-a098-b8971c02ebef",
"iat": 1652556266,
"exp": 1653161066,
"iss": "https://codecurated.com",
"name": "Brilian Firdaus",
"email": "brilianfird@gmail.com",
"email_verified": true
}
}
我们已经成功地使用 Javajose4j库创建了 JWT!现在,让我们继续 JWT 消费过程。
要使用 JWT,我们可以使用库JwtConsumer中的类jose4j。让我们看一个例子:
@Test
public void JWS_consume() throws Exception {
String jwt = "eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJzdWIiOiI3NTYwNzU1ZS1mNDVkLTRlYmItYTA5OC1iODk3MWMwMmViZWYiLCJpYXQiOjE2NTI1NTYyNjYsImV4cCI6MTY1MzE2MTA2NiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9jb2RlY3VyYXRlZC5jb20iLCJuYW1lIjoiQnJpbGlhbiBGaXJkYXVzIiwiZW1haWwiOiJicmlsaWFuZmlyZEBnbWFpbC5jb20iLCJlbWFpbF92ZXJpZmllZCI6dHJ1ZX0.";
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer = new JwtConsumerBuilder()
// required for NONE alg
.setJwsAlgorithmConstraints(AlgorithmConstraints.NO_CONSTRAINTS)
// disable signature requirement
.setDisableRequireSignature()
// require the JWT to have iat field
.setRequireIssuedAt()
// require the JWT to have exp field
.setRequireExpirationTime()
// expect the iss to be https://codecurated.com
.setExpectedIssuer("https://codecurated.com")
.build();
// process JWT to jwt context
JwtContext jwtContext = jwtConsumer.process(jwt);
// get JWS object
JsonWebSignature jws = (JsonWebSignature)jwtContext.getJoseObjects().get(0);
// get claims
JwtClaims jwtClaims = jwtContext.getJwtClaims();
// print claims as map
System.out.println(jwtClaims.getClaimsMap());
}
通过使用JwtConsumer,我们可以轻松地制定有关在处理传入 JWT 时要验证的内容的规则。它还提供了一种简单的方法来分别使用.getJoseObjects()和来获取 JWS 对象和声明。getJwtClaims()
现在我们知道如何在没有签名算法的情况下生成和使用 JWT,使用它来理解 JWT 会容易得多。不同之处在于我们需要设置算法并创建一个密钥来生成/验证 JWT。
HMAC SHA-256
HMAC SHA-256( HS256) 是一个具有对称密钥的 MAC 函数。我们需要为其密钥生成至少 32 个字节并将其提供给库中的HmacKey类jose4j以确保安全。
我们将使用SecureRandomJava 中的库来确保密钥的随机性。
byte[] key = new byte[32];
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
secureRandom.nextBytes(key);
HmacKey hmacKey = new HmacKey(key);
密钥应被视为凭证,因此应存储在安全的环境中。作为推荐,您可以将其存储为环境变量或 [Vault](https://www.vaultproject.io/)。
让我们看看如何创建和使用签名的 JWT HS256:
@Test
public void JWS_HS256() throws Exception {
// generate key
byte[] key = new byte[32];
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
secureRandom.nextBytes(key);
HmacKey hmacKey = new HmacKey(key);
JwtClaims jwtClaims = new JwtClaims();
jwtClaims.setSubject("7560755e-f45d-4ebb-a098-b8971c02ebef"); // set sub
jwtClaims.setIssuedAtToNow(); // set iat
jwtClaims.setExpirationTimeMinutesInTheFuture(10080); // set exp
jwtClaims.setIssuer("https://codecurated.com"); // set iss
jwtClaims.setStringClaim("name", "Brilian Firdaus"); // set name
jwtClaims.setStringClaim("email", "brilianfird@gmail.com");//set email
jwtClaims.setClaim("email_verified", true); //set email_verified
JsonWebSignature jws = new JsonWebSignature();
// Set alg header as HMAC_SHA256
jws.setAlgorithmHeaderValue(AlgorithmIdentifiers.HMAC_SHA256);
// Set key to hmacKey
jws.setKey(hmacKey);
jws.setPayload(jwtClaims.toJson());
String jwt = jws.getCompactSerialization(); //produce eyJ.. JWT
// we don't need NO_CONSTRAINT and disable require signature anymore
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer = new JwtConsumerBuilder()
.setRequireIssuedAt()
.setRequireExpirationTime()
.setExpectedIssuer("https://codecurated.com")
// set the verification key
.setVerificationKey(hmacKey)
.build();
// process JWT to jwt context
JwtContext jwtContext = jwtConsumer.process(jwt);
// get JWS object
JsonWebSignature consumedJWS = (JsonWebSignature)jwtContext.getJoseObjects().get(0);
// get claims
JwtClaims consumedJWTClaims = jwtContext.getJwtClaims();
// print claims as map
System.out.println(consumedJWTClaims.getClaimsMap());
// Assert header, key, and claims
Assertions.assertEquals(jws.getAlgorithmHeaderValue(), consumedJWS.getAlgorithmHeaderValue());
Assertions.assertEquals(jws.getKey(), consumedJWS.getKey());
Assertions.assertEquals(jwtClaims.toJson(), consumedJWTClaims.toJson());
}
与在没有签名算法的情况下创建 JWS 相比,代码没有太大区别。我们首先使用SecureRandom和HmacKey类制作了密钥。由于HS256使用对称密钥,我们只需要一个用于签署和验证 JWT 的密钥。
我们还将算法头值设置为HS256by usingjws.setAlgorithmheaderValue(AlgorithmIdentifiers.HMAC_SHA256和 key with jws.setKey(hmacKey)。
在 JWT 消费者中,我们只需要.setVerificationKey(hmacKey)在jwtConsumer对象上使用设置 HMAC 密钥,jose4j就会通过解析其 JOSE 头来自动确定 JWS 中使用的是哪种算法。
ES256
与HS256只需要一个密钥不同,我们需要为ES256算法生成两个密钥,私钥和公钥。
我们可以使用私钥来创建和验证 JWT,而我们只能使用公钥来验证 JWT。由于这些特性,私钥通常存储为凭证,而公钥可以作为 JWK 公开托管,因此 JWT 的使用者可以查询主机并自行获取密钥。
jose4j库提供了一个简单的 API 来生成作为 JWK 的私钥和公钥。
EllipticCurveJsonWebKey ellipticCurveJsonWebKey = EcJwkGenerator.generateJwk(EllipticCurves.P256);
// get private key
ellipticCurveJsonWebKey.getPrivateKey();
// get public key
ellipticCurveJsonWebKey.getECPublicKey();
现在我们知道了如何生成密钥,使用算法创建 JWT 与使用ES256算法创建 JWT 几乎相同HS256。
...
JsonWebSignature jws = new JsonWebSignature();
// Set alg header as ECDSA_USING_P256_CURVE_AND_SHA256
jws.setAlgorithmHeaderValue(AlgorithmIdentifiers.ECDSA_USING_P256_CURVE_AND_SHA256);
// Set key to the generated private key
jws.setKey(ellipticCurveJsonWebKey.getPrivateKey());
jws.setPayload(jwtClaims.toJson());
...
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer = new JwtConsumerBuilder()
.setRequireIssuedAt()
.setRequireExpirationTime()
.setExpectedIssuer("https://codecurated.com")
// set the verification key as the public key
.setVerificationKey(ellipticCurveJsonWebKey.getECPublicKey())
.build();
...唯一不同的是:
- 我们将算法头设置为
ECDSA_USING_P256_CURVE_AND_SHA256 - 我们在创建 JWT 时使用私钥
- 我们使用公钥来验证 JWT
托管 JWK
JsonWebKeySet我们可以使用该类轻松创建 JSON Web Key Set 。
@GetMapping("/jwk")
public String jwk() throws JoseException {
// Create public key and private key pair
EllipticCurveJsonWebKey ellipticCurveJsonWebKey = EcJwkGenerator.generateJwk(EllipticCurves.P256);
// Create JsonWebkeySet object
JsonWebKeySet jsonWebKeySet = new JsonWebKeySet();
// Add the public key to the JsonWebKeySet object
jsonWebKeySet.addJsonWebKey(ellipticCurveJsonWebKey);
// toJson() method by default won't host the private key
return jsonWebKeySet.toJson();
}
我们还需要更改密钥解析器的一些属性:
// Define verification key resolver
HttpsJwks httpsJkws = new HttpsJwks("http://localhost:8080/jwk");
HttpsJwksVerificationKeyResolver verificationKeyResolver =
new HttpsJwksVerificationKeyResolver(httpsJkws);
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer = new JwtConsumerBuilder()
.setRequireIssuedAt()
.setRequireExpirationTime()
.setExpectedIssuer("https://codecurated.com")
// set verification key resolver
.setVerificationKeyResolver(verificationKeyResolver)
.build();
由于我们托管了 JSON Web 密钥集,因此我们需要查询主机。jose4j还提供了一种简单的方法来使用HttpsJwksVerificationKeyResolver.
在 Java 中实现 JWE
JSON Web Encryption 与 JWS 不同,它是一种经过加密的 JWT,除了具有私钥的内容外,没有人可以看到其内容。首先,让我们看一个例子。
eyJhbGciOiJFQ0RILUVTK0EyNTZLVyIsImVuYyI6IkExMjhDQkMtSFMyNTYiLCJlcGsiOnsia3R5IjoiRUMiLCJ4IjoiMEdxMEFuWUk1RVFxOUVZYjB4dmxjTGxKanV6ckxhSjhUYUdHYzk5MU9sayIsInkiOiJya1Q2cjlqUWhjRU1xaGtubHJ6S0hVemFKMlhWakFpWGpIWGZYZU9aY0hRIiwiY3J2IjoiUC0yNTYifX0.DUrC7Y_ejpt1n9c8wXetwU65sxkEYxG6RBsCUdokVODJBtwypL9VjQ.ydZx-UDWDN7jbGeESXvPHg.6ksHUeeGgGj0txFNXmsSQUCnAv52tJuGR5vgrX54vnLkryPFv2ATdLwYXZz3mAjeDes4s9otz4-Fzg1IBZ4qsfCVa6_3CVdkb8BTU4OvQx23SFEgtj8zh-8ZrqZbpKIT.p-E09mQIleNCCmwX3YL-uQ
JWE的结构是:
BASE64URL(UTF8(JWE Protected Header)) || ’.’ ||
BASE64URL(JWE Encrypted Key) || ’.’ ||
BASE64URL(JWE Initialization Vector) || ’.’ ||
BASE64URL(JWE Ciphertext) || ’.’ ||
BASE64URL(JWE Authentication Tag)
如果我们解密 JWE,我们将得到以下声明:
{
"iss":"https://codecurated.com",
"exp":1654274573,
"iat":1654256573,
"sub":"12345"
}
现在,让我们看看我们如何创建 JWE:
@Test
public void JWE_ECDHES256() throws Exception {
// Determine signature algorithm and encryption algorithm
String alg = KeyManagementAlgorithmIdentifiers.ECDH_ES_A256KW;
String encryptionAlgorithm = ContentEncryptionAlgorithmIdentifiers.AES_128_CBC_HMAC_SHA_256;
// Generate EC JWK
EllipticCurveJsonWebKey ecJWK = EcJwkGenerator.generateJwk(EllipticCurves.P256);
// Create
JwtClaims jwtClaims = new JwtClaims();
jwtClaims.setIssuer("https://codecurated.com");
jwtClaims.setExpirationTimeMinutesInTheFuture(300);
jwtClaims.setIssuedAtToNow();
jwtClaims.setSubject("12345");
// Create JWE
JsonWebEncryption jwe = new JsonWebEncryption();
jwe.setPlaintext(jwtClaims.toJson());
// Set JWE's signature algorithm and encryption algorithm
jwe.setAlgorithmHeaderValue(alg);
jwe.setEncryptionMethodHeaderParameter(encryptionAlgorithm);
// Unlike JWS, to create the JWE we use the public key
jwe.setKey(ecJWK.getPublicKey());
String compactSerialization = jwe.getCompactSerialization();
System.out.println(compactSerialization);
// Create JWT Consumer
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer =
new JwtConsumerBuilder()
// We set the private key as decryption key
.setDecryptionKey(ecJWK.getPrivateKey())
// JWE doesn't have signature, so we disable it
.setDisableRequireSignature()
.build();
// Get the JwtContext of the JWE
JwtContext jwtContext = jwtConsumer.process(compactSerialization);
System.out.println(jwtContext.getJwtClaims());
}
与 JWS 相比,创建和使用 JWE 的主要区别在于:
- 我们使用公钥作为加密密钥,使用私钥作为解密密钥
- 我们在 JWE 中没有签名,因此消费者需要跳过签名要求
结论
在本文中,我们学习了使用jose4j. 希望这篇文章对您有用。如果想进一步了解 JWT 的概念,可以访问我的另一篇文章。
how-to-implement-json-web-token-jwt-in-java-spring-boot